The editors of the scientific journal Nature Communications chose the Technion researchers' article as one of the most important studies in recent times
Researchers at the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering at the Technion have developed a new group of meta-fluids - artificial fluids with properties that do not exist in natural materials. The research was led by doctoral student Ofek Peretz, Prof. Amir Gat and Prof. Sefi Gabli from the Faculty of Mechanical Engineering at the Technion. The study was published in Nature Communications, and has now been selected by the editors of the scientific journal as well of the important studies most recently published in it.
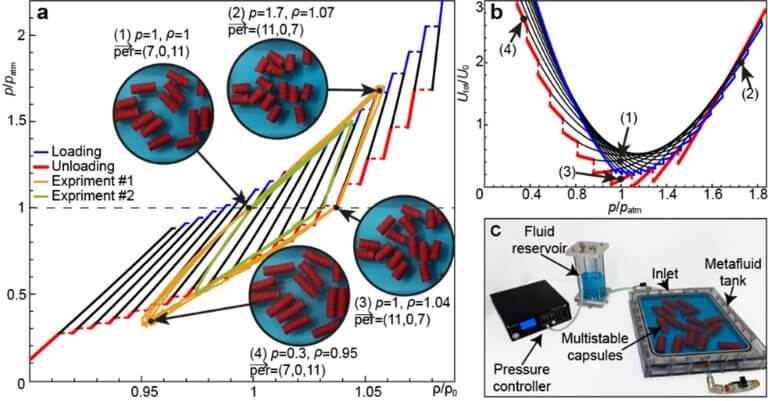
Metafluids are a subset of metamaterials - artificial materials that exhibit new properties that do not exist in natural materials, for example "negative mass", light scattering, vibration damping and excessive flexibility. In the new article, the Technion researchers present new meta-flows, one of whose unique properties is their ability to efficiently harvest energy from the environment and store it in atmospheric conditions. This development has various practical implications, primarily the creation of a non-polluting substitute for coolants used in air conditioners and other cooling systems.
The performance of cooling systems - their efficiency, their range of operation and their environmental consequences - depend on the thermodynamic properties of those liquids. Technion researchers have developed fluids with improved thermodynamic properties, meaning fluids that are not only more efficient but also less polluting. The liquid developed by the Technion researchers is based on capsules that contain gas and are immersed in another liquid. The interaction between the three components of the system determines the thermodynamic properties of the entire system - the meta-flow. The fact that the capsules are multi-stable, meaning they have several stable equilibrium states, gives the liquid unique thermodynamic properties, including storing and releasing energy and removing heat from the environment.
Refrigeration is a field of activity that is considered the biggest environmental polluter, and this is due to the liquids used in it. That's why the Technion researchers estimate that the development will contribute significantly to reducing environmental pollution emissions and reducing man's part in global warming. The doctoral student Ofek Peretz Prof. Sefi Gabli Prof. Amir Gat
The research was supported by the National Science Foundation.
For an article in the journal Nature Communications click here
More of the topic in Hayadan:
- "A computer can read and understand contracts, the lawyers will be able to do strategic work"
- Researchers from the Hebrew University and Switzerland have developed a new experimental method for characterizing liquids found in the depths of the earth
- Students from around the US chose a name for a new component to be launched to the space station - "Harmony"
- Panic button
- Things people know: why are insects small?
