Hayadan > Biology and Medicine
Biology and Medicine
- Dr.Roey Tsezana
- April 25, 2024
The Light Bio company has developed petunia plants that contain a lighting garden of fireflies. Will they give up the street lights?
- Weizmann Institute
- April 24, 2024
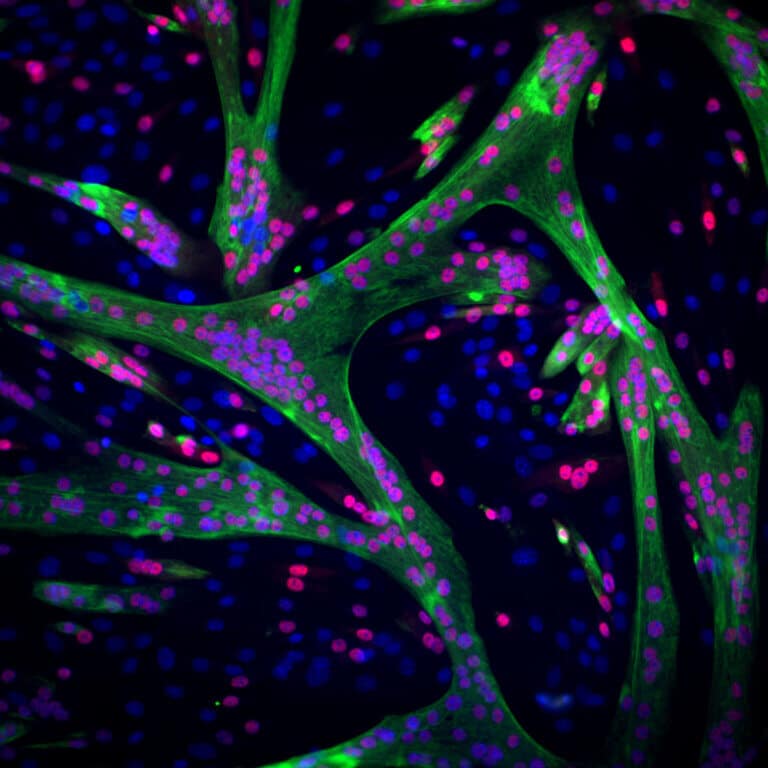
An artificial intelligence model sheds light on the specialization pathway of muscle cells and reveals an important control node along the way
- Weizmann Institute
- April 22, 2024
Research in field mice under conditions simulating a natural environment reveals the different strategies used by females and males in creating social hierarchies
- The Technion
- April 20, 2024
- No comments
The intestine is a very dynamic organ that is constantly changing structurally, mechanically and chemically, and the intestinal bacteria are required to cope with this dynamism. One of the features that may help them in this is plasticity - the ability to undergo rapid genomic changes in response to changes in environmental conditions
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- April 20, 2024
- One response
Prof. Oren Levy researches the timing of the reproduction of corals around the world and is surprised by Dioc. However the biological clock of the corals is not adapted to the volume lights
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- April 19, 2024
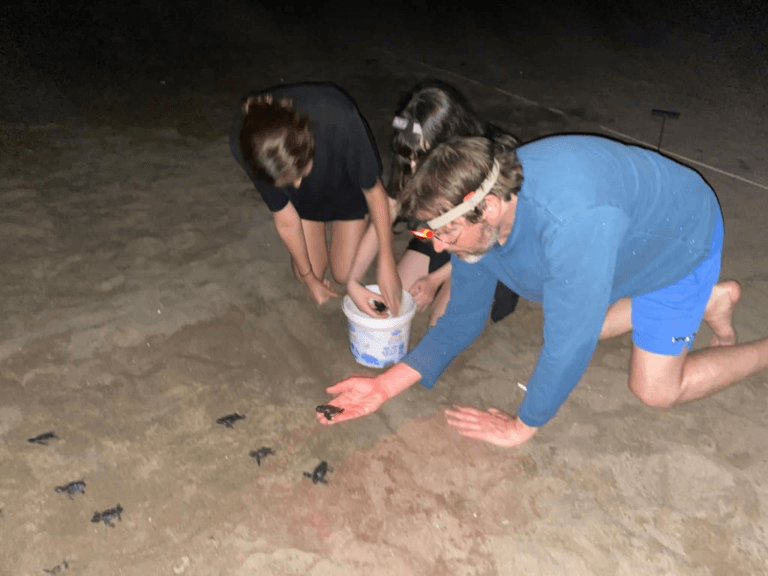
Researchers analyze the DNA and hormonal profile of the green turtles to understand their physiology, development and reproduction and ensure their survival
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- April 17, 2024
A study found that people who were exposed to emotional images reacted according to the reactions of others and judged harshly those who did not react like everyone else
- Dr.Roey Tsezana
- April 14, 2024
The Cow of Heaven project aims to find a way to produce milk protein from bacteria that feed on carbon dioxide and hydrogen
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- April 14, 2024
Theater researchers examined the reception of the Haifa International Festival for Children's Plays
- Tel Aviv University
- April 6, 2024
The research team: "We must act quickly to continue protecting our coral reefs" * The article is dedicated to the memory of Tal Ilon, a man of the sea, the commander of the Kfar Gaza alert squad who was murdered on October 7
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- April 5, 2024
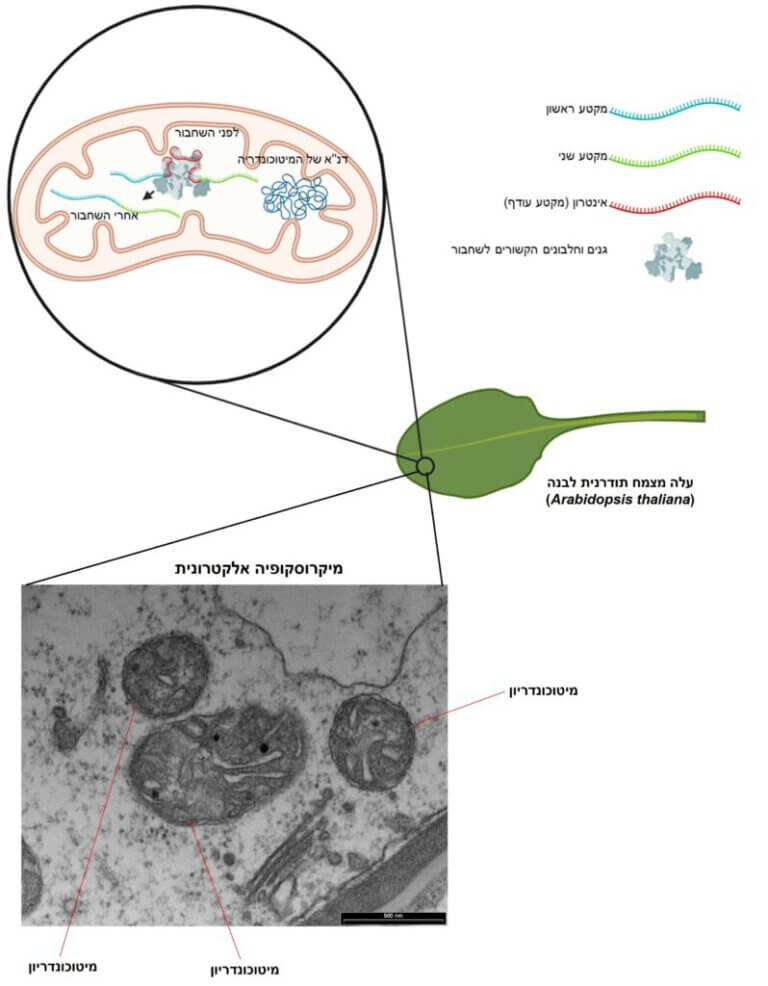
Researchers have characterized genes and proteins that are involved in the splicing process in the mitochondria of plants and are essential for cellular respiration and growth
- Weizmann Institute
- March 28, 2024
- Dr.Roey Tsezana
- March 28, 2024
An American farmer who illegally cloned a giant sheep - and tried to develop a new hybrid species throughout the United States and release it into the wild
- Tel Aviv University
- March 28, 2024
Fish that change their distribution towards the poles due to climate change are declining in abundance
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 27, 2024
- 2 תגובות
Unlike the 2017 eclipse that occurred in August, this eclipse occurs when the spring migration is already underway. And since most birds fly at night, a solar eclipse may affect them significantly
- Tel Aviv University
- March 27, 2024
Why did the ancient man return again and again, over hundreds of thousands of years, to the same quarry sites? It turns out that the secret lies in the migration routes of the elephants
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 26, 2024
- No comments
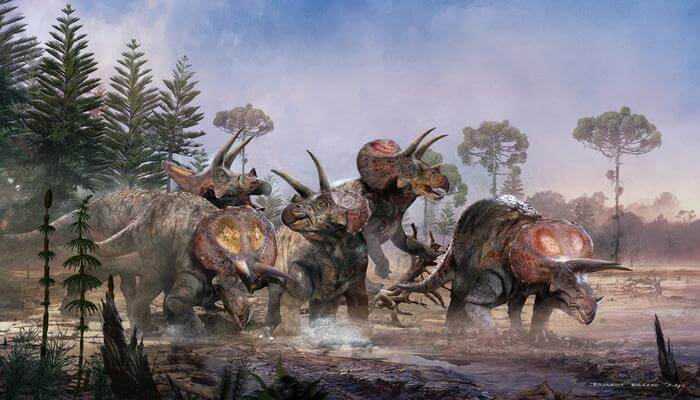
A decade-long study shows that five three-horned dinosaurs lived - and died - together, similar to their depiction in Steven Spielberg's Jurassic World
- Haifa University
- March 26, 2024
- No comments
According to the researchers, the dolphins communicate in a different way and change their vocal behavior when they encounter the noise of a ship and therefore they are definitely affected by the noise of the ships. Past studies have already shown that a change in vocal behavior can be related to stress and distress
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 25, 2024
- No comments
Researchers report new compounds that appear to be able to mimic the physical drive of exercise—at least in rodent cells. This discovery could lead to a new way to treat muscular dystrophy and other medical conditions in humans, including heart failure and neurodegenerative diseases
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 24, 2024
- One response
The loss of the tail occurred about 25 million years ago, when the lineage of humans and great apes split from that of the ancient apes. The researchers identified the insertion of a specific AluY element into the intron of the TBXT gene as a key event that could explain the loss of the tail
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 22, 2024
- No comments
Dutch researchers found that this process happens all the time and damages all genes, but the longer the genes, the more likely they are to be damaged because they have more sites. Especially the great damage is to nerve cells due to their inability to regenerate
- Tel Aviv University
- March 21, 2024
This is how the decision-making mechanism of viruses works
- Weizmann Institute
- March 20, 2024
Scientists of the Weizmann Institute of Science have discovered a new species of Schmer that is able to push the legs of other species that may be dangerous to health; The scientists named the new species after Dr. Chaim Weizman
- Avi Blizovsky
- March 18, 2024
- No comments
Neurological morbidity is the world's number 1 cause of morbidity and disability, with over 3 billion people with brain diseases * according to an article published this weekend in the Lancet. The scope of morbidity and disability has grown since 1990 by 18%
- The Voice of Science website - the Israel National Science Foundation
- March 14, 2024
Researchers discovered which genes are required for each stage of cell differentiation into neural stem cells and neurons, i.e. for brain development, and which of them are involved in diseases of the nervous system