The first seismological measurements of the Insight were made near the landing of the spacecraft in September 2021. Among the seismic records were also two tremors on the other side of Mars that originated from a meteorite hitting its ground
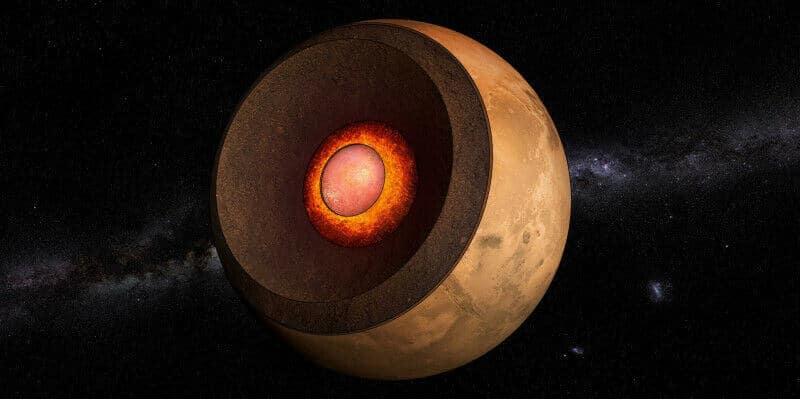
A combination of the analysis of the Martian earthquakes measured by the American Mars lander Insight and computer simulations that illuminate the interior of Mars in a new light, it became clear that between the core of the planet made of liquid iron and the shell of solid silica there is a layer of magma - liquid silicate there is a layer of magma - Liquid silicate 150 km thick. In comparison, Earth does not have a completely liquid silicate layer.
A preliminary analysis of the earthquakes on Mars showed that the average density of the Martian core is significantly less than that of liquid iron. For comparison, the core content of the earth contains 90% iron and these elements and the balance includes light elements such as sulfur, carbon, oxygen and hydrogen. The initial estimates regarding the core of Mars that these elements are in the scope of 20%. These estimates raise many questions because they are not reasonable. Recent estimates show that the diameter of the core of Mars is between 1700 - 1650 km smaller than previous estimates of 1850 - 1800 km. According to recent estimates, if the Martian radium is smaller, then its density should be greater.
According to the new calculations, the amount of light elements in the nucleus is between 9% - 14% and not 20%. The very fact that there is a significant amount of light elements in the core, according to the researchers' assessment, indicates that in an early stage of the formation of the solar system, when it was surrounded by a gas nebula from which the light elements were formed that could accumulate in the core of Mars.
The first seismological measurements of the Insight were made near the landing of the spacecraft in September 2021. Among the seismic records were also two tremors on the other side of Mars that originated from a meteorite hitting its ground. The question arises, what was the size of this body. If it is a body that is a few meters in diameter, it is hard to believe that it will have a big impact on the seismic record. Since Mars is currently surrounded by a fleet of spacecraft. It may be that an archival examination of photographs taken by these spacecraft will enable this type of examination. The intention is to locate photographs that were taken following the pointing of the spacecraft's cameras into space itself and also those that followed the movement of meteors that penetrated the atmosphere. In this way it will be possible to measure their size and hence to estimate their weight and their effect on the seismic records.
Barbara Vonarburg – “Mystery of Martian core solved” 26.10.2023

One response
It's such a shame they fired the proofreading department
In "Yaden"...
Actually there were cute people...
(except that _&₪'*₪_554_&:*”#&@3456…)