The laureates discovered mechanisms that repair DNA damage to maintain the integrity of the cell - one during the current activity of the cell (damages from smoking, exposure to the sun and carcinogens) and the other corrects mistakes during cell division
Avi Blizovsky and Dr. Moshe Nachmani
The Nobel Prize Committee decided to award the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for 2015 to three researchers, Thomas Lindahl from Sweden, Paul Modritz from the USA and Aziz Sanger from Turkey who significantly advanced our understanding of the repair mechanisms of the most important biological material for humans - DNA.
The three researchers were able to map, at the molecular level, the mechanism by which cells repair damaged DNA and thereby protect the genetic information stored within it. Their work provided comprehensive knowledge regarding the functioning of living cells, and more importantly, for the development of innovative treatments against cancer.
Every day, our DNA is damaged as a result of exposure to ultraviolet radiation from the sun, free radicals and other carcinogens; And even in the absence of such powerful pests, the DNA molecule, in a structured way, is an unstable molecule. Thousands of spontaneous changes in the cell's genome occur every day. Moreover, defects in DNA may also occur when the molecule itself is copied during cell division, a process that occurs in the human body millions of times every day.
The reason our genetic material does not completely disintegrate into chemical chaos is a multitude of molecular systems that continuously monitor and repair the DNA. The 2015 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to three pioneering scientists who were able to map how several such repair systems work at the cellular level
The winners of the 2015 Nobel Prize in Chemistry provided basic insights into the way cells function, knowledge that is used, among other things, in the development of new cancer drugs.
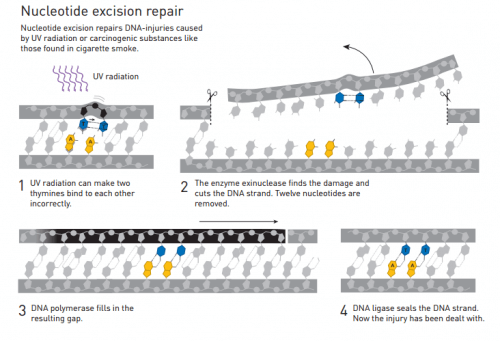
In the early XNUMXs, researchers believed that DNA was a particularly stable molecule, but the researcher Thomas Lindahl demonstrated that the molecule breaks down at a rate that must have enabled the existence of life on Earth. This insight led him to discover a cellular mechanism called "base excision repair, BER", a mechanism that regularly neutralizes the complete breakdown of DNA.
The researcher Aziz Sanger mapped this repair mechanism, with the help of which the cells repair the damage caused to the DNA as a result of their exposure to ultraviolet radiation. People born with defects in this repair mechanism will develop skin cancer over many years when exposed to sunlight. This mechanism is also used in cells to repair DNA defects caused by exposure to carcinogenic substances.
Researcher Paul Modritz showed how the cell corrects the errors that occur when DNA is replicated and copied during the important step of cell division. This mechanism, known as "mismatch repair", reduces the frequency of errors during DNA replication by a factor of thousands. Congenital defects in this repair mechanism are known in the literature, and some of them lead to the hereditary version of colon cancer.
Thomas Lindahl, a Swedish citizen born in Stockholm in 1938 is Professor Emeritus at the Francis Crick Institute in London and former Director of Cancer Research UK. Paul Modrich, an American citizen born in 1946, received his doctorate at Stanford University and is currently a researcher at the Howard Hughes Medical Institute at Duke University School of Medicine. Aziz Sankar, American and Turkish citizen and born in Turkey. He received his doctorate in 1977 from the University of Texas and is currently a professor of biochemistry and biophysics at the University of North Carolina.
Expansion later today.
Nobel 2015
Bacteria and plants against parasites - drug developers against tropical diseases won the Nobel Prize in Medicine for 2015 - Drug developers against tropical diseases won the 2015 Nobel Prize for Medicine
