At the Institute for Space Research at the Technion, a design survey was held, in which the development of the "Samson" project was presented
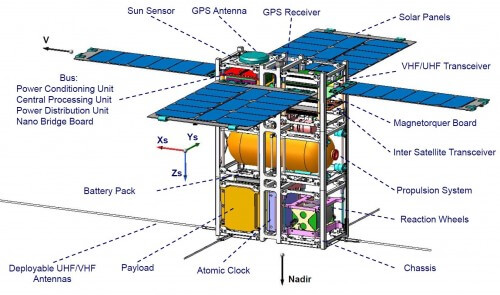
On June 18, the CDR (Critical Design Review) of the "Samson" project took place at the Technion Space Research Institute - the first launch of three nanosatellites in a cluster flight. In the survey, which is a kind of critical milestone towards the construction of the satellites, the scientific missions and all the subsystems were presented.
The "Samson" project, which is a pioneering project in the field of distributed satellites, includes three tiny satellites, which will be transported at an altitude of about 700 kilometers above the earth in an autonomous cluster flight. This means that the satellites will maintain a controlled structure in space, through inter-satellite communication and correcting their orbits independently.
The main mission of "Samson" is to prove the feasibility of a cluster flight of nanosatellites in space, and the second - to accurately locate people and ships in distress. The research is led by Professor Finny Gurfil, and the construction of the satellites by system engineer Avner Kider. The ground station, as well as the radiating source (which simulates the person in need of rescue) will be located at the Technion.
"The Technion gave us a huge mandate: to design a first-of-its-kind system, build it and launch it into space," said the head of the Space Research Institute, Professor Ehud Bacher. "In addition, the Technion provides the lion's share of our budget. However, this is a large and very complex project, which we could not carry out without partners within the Technion (the Space Research Institute, the Faculty of Aeronautics and Space Engineering, the Communications Laboratory in the Faculty of Electrical Engineering) and outside the Technion (the Aerospace Industry, Rafael, the Ministry of Science and the Israel Space Agency, Ort Brauda) . Therefore, as far as we are concerned, we are leading a national project here."
Professor Bacher said that "This is a very pretentious project, with high risk, a rigid schedule and a huge expectation of success, so this is the closest thing to a start-up I have done in my career. And of course it is especially complicated because there is a significant element of hardware here."
Professor Gurfil explained that the systems in the three satellites will be powered by solar energy, and the satellites will be powered by a high-pressure compressed gas propulsion system.
The launch of the three Samson satellites is planned for the first half of 2016, as an additional payload through one of the commercial launches. The Space Research Institute is in negotiations with several launch parties around the world with the goal of signing a launch contract soon.

12 תגובות
It is possible that the state will participate in three thousand
Water blowing
Even if you get a brain from Gaza, even fourth hand, it won't help. Cognitively, you are a total loss. You should be sent to the scrapyard.
There are now probably at good prices, maybe second hand from Gaza
Water blowing
I understand your lobotomy failed. Maybe do a brain swap. I doubt it will help.
Distinguished people, if they calculate one beam without crossing, due to the great speed of the beam and the "slow" speed of the processors, they are not able to feel a distance smaller than thirty smets, with respect to blowing water
Suppose I claim that the speed of light decreases by XNUMX cm per second per year. Let's just say. As for GPS, it shouldn't be a problem. A measurement error of a meter for another hundred years. Regarding gravitational waves that are also being searched for, it seems to me that the accuracy should be greater.
And I understand that there is no ceasefire
So that's it!
But I will still wish everyone:
Good night!
Sabdarmish Yehuda
Sabdarmish Yehuda
GPS satellites give an accuracy of meters, and even less than that. This, when the distance to the satellite is tens of thousands of km.
Lasers are used to build very sensitive gyro devices, which are based on precise measurements of the beam's trajectory.
I don't understand what the problem is with measuring distance between satellites with any precision you want. You can perform frequency modulation and get any precision you want.
It is true that in theory the tracks should cross, but it seems to me, without calculating, that the corrections to save space that need to be made are very small.
Yehuda Sabdarmish
A. Do you know a more accurate method for measuring distances with a laser beam?
B. It does not seem that the "Samson" flight is intended for the detection of gravitational waves. The reason:
To detect gravitational waves, the measuring instrument must be in a constant gravitational field.
A device in a changing gravitational field will have difficulty detecting the gravitational waves
measured from space, and separate them from the small changes in the gravitational field
The operator on "Samson" in his flight around KDA.
for miracles
One of the goals of such a flight is the detection of gravitational waves, so the distance between the nano-satellites must be measured very precisely. I doubt if a laser beam will be able to give the required accuracy.
Good night and quiet
Sabdarmish Yehuda
Yehuda
"What would you say to the knowledge that the speed of light may change"... I will say that this knowledge has no effect on the subject.
Why is the project called SAMSON?
It is interesting to receive basic data such as:
A. What is (approximately) the distance between the three nano satellites?
B. What is the size of the allowed/required deviation?
third. What is (approximately) the size and weight of the nano-satellites (according to KDA)?
d. According to the current planning, will their gaze be directed towards space?
The article briefly concerns the problems of glimpses in such a satellite system. They did not talk about the way to determine the exact distance between the three nano-satellites and the difficulties arising from this. Assuming that the distance will be determined by a laser beam, how is this done? What would you say to the knowledge that the speed of light may change. Another important thing is that the satellites move in motion around the center of the earth, therefore their orbits cannot move parallel but must cross each other. The need to determine a parallel route will require continuous investment of energy. Obviously, the amount of this is limited. In short, I would love to receive a much more detailed article on the subject.
Good day and quiet
Sabdarmish Yehuda